I had a chance to interview Aaron Leonard late last September (photo URL) just before he took a leave from his online community management work at the World Bank to talk about that work. This is part of a client project I’m working on to evaluate a regional collaboration pattern and to start understanding processes for more strategic design, implementation and evaluation of collaboration platforms, particularly in the international development context.
Aaron’s World Bank blog is http://www.southsouth.info/profiles/blog/list?user=1uxarewp1npnk
How long have you been working on “this online community/networks stuff” at the Bank? How did your team’s practice emerge?
I’ve been at the bank 4 years and working on their communities of practice (CoP) front for 3 of those. I started as a community manager building a CoP for external/non-bank people focused onSouth-South exchange. Throughout this process, I struggled with navigating the World Bank rules governing these types of “social websites”. At the time, there were no actual rules in place – they were under formulation. So what you could do,/could not, use/ could not, pay for/ could not depended on who you talked to. I started working with other community managers to find answers to these questions along with getting tips and tricks on how to engage members, build HTML widgets, etc… I realized that my background working with networks (pre-Bank experience) and my experience launching an online community of practice within the Bank was useful to others. As more and more people joined our discussions, we started formalizing our conversation (scheduling meetings in advance, setting agendas, etc… but not too formal :).
We were eventually able to make ourselves useful enough to the point where I applied for and received a small budget to bring in some outside help from a very capable firm called Root Change and to hire a brilliant guy, Kurt Morriesen, to help us develop a few tools for community managers and project teams and to help them think through their work with networks. We started with 15 groups – mostly within WBI, but some from the regions as well. All were asking and needing answers to some common questions, “How do we get what we want out of our network? How do we measure and communicate our success? How do we set up a secretariat and good governance structure?” This line of questioning seemed wrong in many ways. It represented a “management mindset” (credit Evan Bloom!) versus a “network mindset”. The project teams were trying to get their membership to do work that fit their programmatic goals versus seeing the membership as the goal and working out a common direction for members to own and act on themselves. We started asking instead, “Why are you engaging? “Who really are you trying to work with?” What do you hope to get out of this engagement?” What value does this network provide its members?” This exercise was really eye opening for all of us and eventually blossomed into an actual program. I brought in Ese Emerhi last year as a full time team member. She has an amazing background as a digital activist, and knows more than I do about how to make communities really work well.
Ese and I set up a work program around CoPs and built it into a practice area for the World Bank Institute (WBI) together with program community managers like Kurt, Norma Garza (Open Contracting), and Raphael Shepard (GYAC) among others. With Ese on board, we were able to expand beyond WBI (to the World Bank in general). This was possible in part because our team works on knowledge exchange, South-South knowledge exchange specifically (SSKE). We help project teams in the World Bank design and deliver effective knowledge exchange. CoPs are a growing part of this business, in part because the technology to connect people in a meaningful conversation is getting better, and in part because we know how to coach people on when and how to use communities.
How did you approach the community building?
With Rootchange we started with basic stocktaking and crowd sourcing with respect to trying to define an agenda for ourselves. We had 4-5 months for this activity. We settled on a couple things.
Looking at different governance arrangements. How do we structure the networks?
What tools or instruments to use in design of planning of more effective networks.
We noticed that we were talking more about networks than communities. Some were blends of CoPs, coalitions, and broader programs. The goals aren’t always just the members’. So we talked about difference between these things, how they can be thought of along a spectrum of commitment or formality. A social network vs. an association and how they are/are not similar beasts.
We gave assignments to project teams and met on monthly basis to work with these instruments. On the impetus of consultants at Root Change, we started doing 1 to 1 consultation w/ teams. We reserved a room, brought in cookies and coffee and then brought the teams in for 90 minutes each of free consulting sessions. These were almost more useful for the teams than the project work. Instead of exploring the tools, they were APPLYING the tools themselves. It was also a matter of taking the time to focus, sit down and be intentional with their work with their networks. Just shut the door and collectively think about what is was they were trying to do. A lot of this started out in a more organic way around what was thought to be an easy win. “We’ll start a CoP, get a website, get 1000 people to sign” up without understanding what it meant for membership, resourcing, team, commitment and longer term goals and objectives.
We helped them peel back some of the layers of the onion to better understand what they were trying to do. We didn’t get as far as wanted. We wanted to get into measuring and evaluation and social network analysis, but that was a little advance for these teams and their stage of development. They did not have someone they could rely on to do this work. Some had a community manager but most of these were short term consultants, for 150 days or less, and often really junior people who saw the job as an entry level gig. They were often more interested in the subject matter than being a community managers. They often tended to get pulled in different directions and may or may not have liked the work. They tended to be hired right out of an International Devevlpment masters program where they had a thematic bent so they were usually interested in projects, vs organizing a 1000 people and lending some sense of community. Different skill sets!
We worked with these teams, and came up with a few ideas,. Root Change wrote a small report (please share) which helped justify a budget for subsequent fiscal year and my boss let me hire someone who would have community building as part of their job. Together we were working on the Art of Knowledge Exchange toolkit and the other half time was for community. At this point we opened up our offering to World Bank group to help people start, understand how to work with membership, engage, measure and report on a CoP. We helped them figure out how they could use data and make sense of their community’s story. We brought in a few speakers and did social things to profile community managers. Over the course of the year we had talked to and worked with over 300 people. (Aaron reports they have exact numbers, but I did not succeed in connecting with him before he left to get those numbers!). We did 100 one-on-one counseling sessions. We reached very broadly across institution and increased the awareness of the skillset we have in WBI regarding communities and networks. We helped people see that this is different way of working. Our work coincided with build up of the Bank’s internal community platform based on Jive (originally called Scoop and now called Sparks – a collaboration for development and CoP oriented platform.) The technology was getting really easy for people to access. There was more talk about knowledge work, about being able to connect clients, and awareness of what had been working well on the S-S platform.
We did a good job and that gave us the support for another round of budget this year. Now we have been able to shift some of the conversation to the convening and brokering role of the Bank. This coincided with the Bank’s decreased emphasis in lending and increase in access to experts which complimented the direction we were going in. We reached out and have become a reference point for a lot of this work. There have been parallele institutional efforts that flare and fade, flare and fade. But it is difficult to move “the machine.” It can even be a painful process to witness. I admire the people doing this, but (the top down institutional change process) was something we tried to avoid. We did our work on the side, supporting people’s efforts where possible. Those things are finally bearing fruit. We have content. They have a management system. We have process for teams to open a new CoP space, a way to find what is available to them as community leaders, They have a community finder associated with an expert finder. Great to have these things to have and invest in, but it is not where we were aiming. We want to know the community leaders, the people like Ese, like Norma Garza, running these communities and who struggle and have new ideas to share. What are the ways to navigate the institutional bureaucracy that governs our use of social media tools? How do you find good people to bring on board. You can’t just hire the next new grad and expect it to last. There is an actual skills set, unique, not always well defined but getting more recognition as something that is of value and unique to building a successful CoP. There is new literature out there and people like Richard Millington (FeverBee) – a kid genius doing this since he was 13. He takes ideas from people like you, Wenger and Denning. There is now more of a practice around this.
While the Bank is still not super intentional on how it works internally with respect to knowledge and process, more attention is being paid and more people are being brought in. It can be a touch and go effort. We’re just a small piece, but feeling a much needed demand and our numbers prove that. We have monthly workshops (x2 sometimes) that are promoted through a learning registration system and we’d sell the spaces out within minutes. People are stalking our stuff. It is exciting. At same time while it felt like the process of expansion touched a lot of people, convinced/shaped dialog, I also feel we lost touch with the Normas. Relationships changed. We were supporting them by profiling them, helping them communicate to their bosses, so the bosses understood their work, but not directly supporting them with new ideas, techniques, approaches.
We reassessed at end of last year. We want to focus building an actual community again. We started but lost that last year while busy pushing outwards. But we still kept them close and we can rely on each other. It has not been the intimate settings of 15-20 or 3 of us doing this work, sitting around and talking about what we are struggling with. Like “how did you do your web setup, how to do a Twitter Jam?” So our goals this year are a combination. Management likes that we hit so many people last year. They have been pretty hands off and we can set our own pace. Because we did well last year, they given us that room, the trust.
So now we want to focus more on championing the higher level community managers. The idea is to take a two fold approach. First we want to use technology to reach out, to use our internal online space to communicate and form a more active online community. We secondly want to focus a few of our offerings on these higher level community managers with idea that if we can give them things to help their with the deeper challenges of their job, they will be able to help us field the more general requests for the more introductory offerings. Can you review my concept note? Help me setting up my technology.
It is still just the two of us. We are grooming another person but also working with the more senior community managers will allow us to handle more requests by relying on their experience. We give them training and in return they help w/ basic requests. This is not a mandate. We don’t have to do this. It is what we see as a way of building a holistic and sustainable community within the Bank to meet the needs of community managers and people who use networks to deliver products and services with their clients.
How do you set strategic intentions when setting up a platform?
One of the things I love most advising about CoPs is telling them not to do it. I love being able to say this. The incentives are wrong, the purpose. So many people think CoPs are something that is “on the checklist, magic bullet, or a sexy tech solution”. Whatever it is, those purposes are wrong. They are thinking about the tech and not the people they are engaging.. If you want to build a fence, you don’t go buy a hammer and be done with it. You need to actually plan it out, think about why you are building it. Why its going in, how high, … bad analogy. To often CoPs are done for all the wrong reasons. The whole intent around involving people in a conversation is lost or not even considered, or is simply an afterthought. The fallacy of “build it and they will come.” One of my favorite usage pieces is from the guy who wrote the 10 things about how to increase engagement on your blog. It speaks to general advice of understanding who you are targeting. Anyone can build a blog, set up a cool website or space. But can you build community? The actual dialog or conversation? How do you do that?
One key is reaching people where they already are – one of the best pieces of advice I’ve heard and I always pass on. Don’t build the fancy million dollar custom website if no one is really going to go there. One of the things I have is a little speech for people. Here’s my analogy. If you are going to throw a party, you have to think about who you are going to invite, where to do it, what to feed them, the music: you are hosting that party. You can’t just leave it up to them. They might trash your place, not get on board, never even open door. You have to manage the crowd, facilitate the conversation unless they already know each other. And why are you throwing the party if they already get together in another space?
Coming from NGO world, and then coming to bank I saw how easy it is to waste development dollars. It is frustrating. I have spoken openly about this. The amount of money wasted on fancy websites that no one uses is sad. There are a lot of great design firms that help you waste that money. It is an easy thing for someone to take credit for a website once it launches. It looks good, and someone makes a few clicks, then on one asks to look at it again. The boss looks at it once and that is it. No one thinks about or sees the long term investment. They see it as a short term win.
One of the things I try to communicate is to ask, if you are going to invest in a platform, do you really want to hear back from the people you are pushing info to? If not build a simple website. If you do want to engage with that community, to what extent and for what purpose? How will you use what you learn to inform your product or work? If you can’t answer that, go back to the first question. If they actually have a plan – and their mandate is to “share knowledge’ – how do they anticipate sharing knowledge. They often tell me a long laundry list of target audiences. So you are targeting the world? This is the conversation I’ve experienced, with no clear, direct targeting, or understanding of who specifically they are trying to connect with. We suggest they focus on one user group. Name real names. If you can’t name an individual or write out a description. Talk about their fears, desires, challenges, and work environment. Really understand them in their daily work life. Then think about how does this proposed platform/experience/community really add value. In what specific way. It is not just about knowledge sharing. People can Google for information. You are competing w/ Google, email, facebook, their boss, their partner. That’s your competition. How do you beat all those for attention. That is what you are competing with when someone sits down at the computer. This is the conversation we like to walk people through before they start. The hard part is a lot of these people are younger or temporary staff hired to do this. It is hard for them to go back to boss and say “we don’t know what we are doing” and possibly lose their jobs. There can be an inherent conflict of interest.
How do you monitor and evaluate the platforms? What indicators do you use? How are they useful?
One of the things we don’t do – and this might be a sticking point – we don’t actually run or manage any of these communities. We just advise teams. I haven’t run one for 2 years. Ese has her own outside, but not inside that we personally run beside the community managers’ community and that has been mainly a repository.
We have built some templates for starting up communities, especially for online networks with external or mixed external and internal audiences. We have online metrics (# posts, pageviews, etc) and survey data that we use to tell the story of a community. Often the target of those metrics are the managers who had the decision making role in that community. We try and communicate intentionally the value (the community gives) to members and to a program. We have developed some more sophisticated tools with RootChange, but we didn’t get enough people to use them. Perhaps they are too sophisticated for the current stage of community development. And we can’t’ force people to use them.
It would be fantastic to have a common rubric, but we don’t have the energy or will to get these decisions. We are still in the early “toddler” stage. Common measurement approaches and quality indicators are far down the line. Same with social network analysis. RootChange has really pushed the envelope in that area, but we aren’t advanced enough to benefit from that level of analysis. The (Rootchange) tool is fun to play around with and provides a way of communicating complex systems to community owners and members. What RootChange has done is is develop an online social network analysis platform that can continuously be updated by members and grow over time. Unlike most SNA, which is a snapshot, this is more organic and builds on an initial survey that is sent to the initial group and they forward it to their networks.
If you had a magic wand, what are three things you’d want every time you have to implement a collaboration platform?
If I had a magic wand and I could actually DO it, I would first eliminate email. Part of the reason, the main reason we can’t get people to collaborate is that they aren’t familiar working in a new way. I think of my cousins that 10 years younger and they don’t have email. They use Facebook. They are dialoging in a different way. They use Facebook’s private messaging, Twitter, and Whatsapp. They use a combination of things that are a lot more direct. They keep an open running of IM messages. Right now email is the reigning champion in the Bank and if we have any hope of getting people to work differently and collaboratively we have to first get rid of email.
Next, to implement any kind of project or activity in a collaboration space right I’d want a really simple user interface, something so intuitive that it just needs no explanation.
Thirdly, I’d’ want that thing available where those people are, regardless if it is on their cell phone, ipad, and any touchable, interactable interface. Here you have to sit at your computer. We don’t even get laptops. You have to sit at desk to engage in online space. Hard to do it through your phone – not easy. People still bring paper and pencil to meetings. More bringing ipads. Still a large minority. A while back I did a study tour to IDEO. They have this internal Facebook like system which shares project updates, findings and all their internal communications called The Tube. No one was using it at the beginning. One of the smartest thing they did was installed – in 50 different offices.- a big flat screen at each entrance. which randomly displays the latest status updates pulled from Tube from across their global team. Once they did that, the rate of people updating their profile and using that as a way of communicating jumped to something like a 99% adoption rate in short time. From a small minority to vast majority. No one wanted to be seen with a project status update from many months past. It put a little social pressure in the commons areas and entrance way – right in front of your bosses and teammates. It was an added incentive to use that space.
You want something simple, that replaces traditional communications, and something with a strong, and present, incentive. When you think about building knowledge sharing into your review – how do you really measure that? You can use point systems, all sorts of ways to identify champions. Yelp does a great job at encouraging champions. I have talked to one of their community managers. They have a smart approach to building and engaging community. They incentive people through special offerings, such as first openings of new restaurants, that they can organize. They get reviews out of that. That’s their business model.
We don’t really have a digital culture now. If we want to engage digitally, globally we have to be more agile with how we use communication technology and where we use it. The tube in front of the urinals and stall doors. You’ve got a minute or two to look at something. That’s the way!
 Gender keeps coming up in my work a lot lately, both as a theme for meetings and work, but also in my lived experience. I have a colleague who has taken over one of my clients because we both feel the client will take on the coaching and feedback better from another man than from me. In a conversation about social capital related investments, another colleague says his rule of thumb is to ad 10% to women they are investing in over the equal-on-paper men just because he knows it pays off. Women’s role in agriculture is finally being recognized in the international development world. And in many cases, it is the development of good data to support these hunches that is finally helping us get traction in USING what we know about gender. So this article comes as no surprise. Don’t stop at the first quote… read to the second one!
Gender keeps coming up in my work a lot lately, both as a theme for meetings and work, but also in my lived experience. I have a colleague who has taken over one of my clients because we both feel the client will take on the coaching and feedback better from another man than from me. In a conversation about social capital related investments, another colleague says his rule of thumb is to ad 10% to women they are investing in over the equal-on-paper men just because he knows it pays off. Women’s role in agriculture is finally being recognized in the international development world. And in many cases, it is the development of good data to support these hunches that is finally helping us get traction in USING what we know about gender. So this article comes as no surprise. Don’t stop at the first quote… read to the second one!

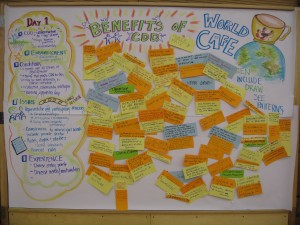
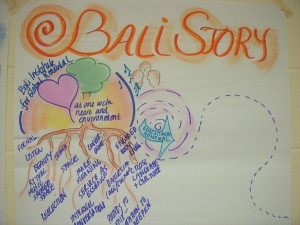
 There are many reasons visual facilitation is important. First of all we have the cognitive value. Our human brains react not just to words (spoken or written) but to images, sounds and even the kinesthetic experience we have as we interact with each other. So including the visual aspects into learning and doing things together enhances a group’s practice and results.
There are many reasons visual facilitation is important. First of all we have the cognitive value. Our human brains react not just to words (spoken or written) but to images, sounds and even the kinesthetic experience we have as we interact with each other. So including the visual aspects into learning and doing things together enhances a group’s practice and results.
 We often think of the visuals as the content of the curriculum, but they are also “receptacles” of interaction. They can be a rich part of our process. Visuals help both the teacher and the learner to listen to each other and, when the conversational artifacts are captured as a visual practice, to show that people have been heard. We can use them between participants to foster better small group work, especially with people who are shyer to talk, or may need to stimulate other parts of their brain to engage and learn. Consider what would happen if you captured learner feedback on a white board visually (not just words) to help understand their understanding, and to demonstrate your listening as a teacher — what kind of a reaction might you expect from the learners? I bet it will be very gratifying and enlightening. I often use
We often think of the visuals as the content of the curriculum, but they are also “receptacles” of interaction. They can be a rich part of our process. Visuals help both the teacher and the learner to listen to each other and, when the conversational artifacts are captured as a visual practice, to show that people have been heard. We can use them between participants to foster better small group work, especially with people who are shyer to talk, or may need to stimulate other parts of their brain to engage and learn. Consider what would happen if you captured learner feedback on a white board visually (not just words) to help understand their understanding, and to demonstrate your listening as a teacher — what kind of a reaction might you expect from the learners? I bet it will be very gratifying and enlightening. I often use