Dang, it was fun to run into this draft from 2016 with links to three terrific posts that amplify something that has shown up in my work over and over again about the need to creatively destroy our patterns that conserve old ways of working that are no longer relevant in today’s (or tomorrow’s) world(s). And happily, all the posts are still online.
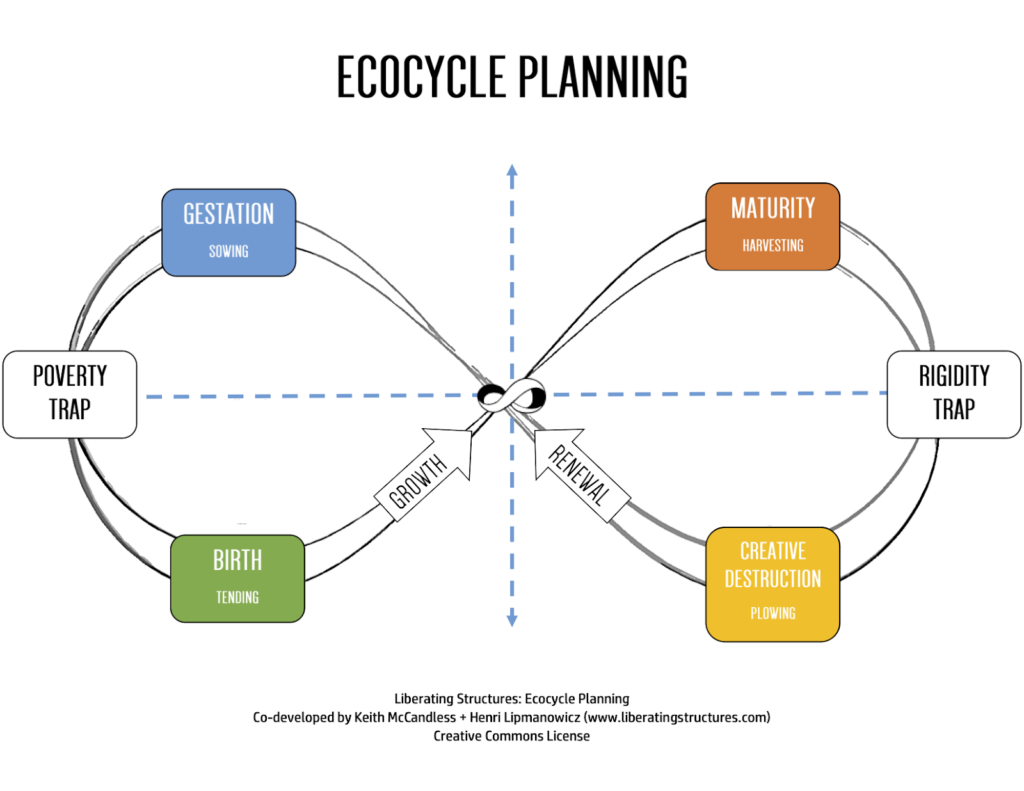
Time and again when working with clients where we’ve used Ecocycle Planning, the richest insights are what shows up in the “rigidity” and the “scarcity” traps (old image below- it used to be called “poverty trap” but there are racist roots there…) The rigidity trap helps us see what is no longer adding value and if we can move past that trap into creative destruction, we can clear away and make space for what is now possible. Too often organizations just add on new things (processes, projects, approaches, rules), layer after layer until we spend all our time ticking boxes with little to show for our time, energy (and peace of mind!)
The first from Simon Terry‘s blog archives, Killing the Golden Goose: From Waste to Potential focuses on the waste created in management that tries to conserve what is working, to the point of ignoring it is no longer working. It is a great read. With an interesting metaphor!
When managers focus on growing human potential to improve effectiveness, this growth mindset redefines the game and pushes changes in the other systems that define our modern organisations. Purpose and goals come first. Engagement is no longer an after thought. Experimentation is a core practice. Collaboration and cooperation are seen as human opportunities to work and not sources of waste & distraction. Volatility is embraced as a source of potential learning. Most importantly of all the new narrative respects and embraces the potential of all in organisations to lead and to contribute.
Killing the Golden Goose: From Waste to Potential, Simon Terry
The second from the fabulous Eugene Eric Kim on Principles for Effecting Change in Complex Social Systems. Eugene harkens back to a post from the wonderful Ruth Rominger “Effecting Change in Complex Social Systems” with Hilary Bradbury, Sissel Waage, and David Sibbet. Of the five principles Eugene refers to, one again tickles that creative destruction idea:
“Surface discontents, build capacity, and elevate expectations. Successful change emerges from dissatisfaction with current conditions, but also celebrates many small victories as well as personal learning, thereby continually building momentum for innovation toward a preferred future.“
Principles for Effecting Change in Complex Social Systems, Eugene Eric Kim
Finally, the inimitable Johnnie Moore ties this overwork (and useless work) to stress and what that destroys, all while chasing efficiencies in “Waste, potential and sticking your neck out.” Plus it links to Simon’s post. It’s all connected! And another fun metaphor.
I see many organisations struggling to get a quart of productivity into a pint pot of systems, under great stress to make savings and be more efficient. I’d suggest that as that stress rises, so does the number of management abstractions bandied about: people only feel safe to talk in general terms about things like “leadership” because if they got specific the whole stressed out deck of cards might come falling down. In these circumstances, meetings become a workaholic microcosm of the organisation – we fill the walls with masses of post-it notes as if this is the measure of the value of our conversations. We can talk in general terms about the need to “manage upwards” or “creating a no-blame culture” but this actually becomes a way of avoiding actually doing it.
via Waste, potential and sticking your neck out | Johnnie Moore.