 This afternoon I’m spending a half hour on a Skype video conversation to share a bit of how I use social media. I figured it would be good to exercise my memory a bit and unearth some of the key stories that led me to to my social media use today, and perhaps surface some of my patterns. The history approach also shows that while the term “social media” was not in play when I jumped in, the social use of online media has been growing for many years – well before my online time. These roots are significant because our patterns of use, our ways of embracing or rejecting technology are grounded in this history.
This afternoon I’m spending a half hour on a Skype video conversation to share a bit of how I use social media. I figured it would be good to exercise my memory a bit and unearth some of the key stories that led me to to my social media use today, and perhaps surface some of my patterns. The history approach also shows that while the term “social media” was not in play when I jumped in, the social use of online media has been growing for many years – well before my online time. These roots are significant because our patterns of use, our ways of embracing or rejecting technology are grounded in this history.
Online Community
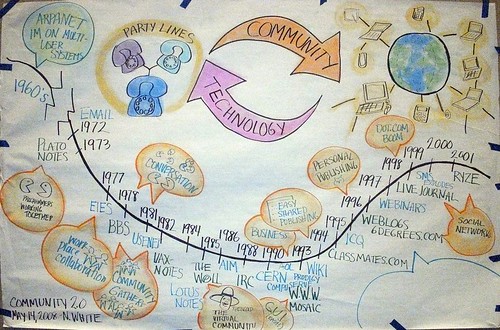 My first real step into what we now call social media was logging on to Howard Rheingold’s “Electric Minds” online community in November 1996. Little did I know that this first toe-dip would literally change the course of my professional, and in many ways, my personal life. I didn’t know what an online community was, even though I have been steeped in community work all my life. All of a sudden I was in the midst of amazing, deep and human conversations with people from across the US and the globe. I remember Ran Avrahami, a professor in Israel, and how he jumped into the conversations and reached out and connected with us. He talked of his grandchildren and the orange trees on his apartment balcony as if he were next door. Of Jay Rosen, who went on to be a pioneer and scholar in online journalism. Of Bodhi in Chicago (who has since passed on) who took this newbie under his wing and who gave me my online name of choconancy.
My first real step into what we now call social media was logging on to Howard Rheingold’s “Electric Minds” online community in November 1996. Little did I know that this first toe-dip would literally change the course of my professional, and in many ways, my personal life. I didn’t know what an online community was, even though I have been steeped in community work all my life. All of a sudden I was in the midst of amazing, deep and human conversations with people from across the US and the globe. I remember Ran Avrahami, a professor in Israel, and how he jumped into the conversations and reached out and connected with us. He talked of his grandchildren and the orange trees on his apartment balcony as if he were next door. Of Jay Rosen, who went on to be a pioneer and scholar in online journalism. Of Bodhi in Chicago (who has since passed on) who took this newbie under his wing and who gave me my online name of choconancy.
 “Eminds” was where I learned that online relationships can be real, how they get real, and how they break and fail. It was in “helping” “save” the community after Howard lost funding that I had my first big online facilitation failure. This taught me about both the similarities and differences of group dynamics online and offline. It was my urgency to figure this out that set me on my professional path as a practitioner and learner about online facilitation. I knew from that experience that whenever we talked about technology (social media) we needed to also talk about practice and the human beings doing the practicing. It was life changing.
“Eminds” was where I learned that online relationships can be real, how they get real, and how they break and fail. It was in “helping” “save” the community after Howard lost funding that I had my first big online facilitation failure. This taught me about both the similarities and differences of group dynamics online and offline. It was my urgency to figure this out that set me on my professional path as a practitioner and learner about online facilitation. I knew from that experience that whenever we talked about technology (social media) we needed to also talk about practice and the human beings doing the practicing. It was life changing.
There are so many lessons from those early days that it is hard to pick out just one or two, but here are the ones that come to mind most quickly and which I remember “in my gut.”
- Social media is a great place to fail. You can try something and if it doesn’t work, learn, adjust and try again. This is true of both the technology and the practices.
- We can find, develop and utilize relationships with other humans online – and they have meaning. But for most of us, it takes an actual transformative experience of this to really believe and embrace it. The gap between the intellectual description and the experience of using social media to build and nurture relationships is large.
Online Learning Together
 The second seminal experience was taking part in George Por’s “Knowledge Ecology University” or KEU as we called it, and the relationship forming event of the KE Fair. This was where I had the amazing opportunity to co-facilitate an online workshop with Mihaela Moussou (now Michele Paradise). Michele and I built on the foundational work of Lisa Kimball (then of Metanet, now of GroupJazz) and began to articulate the practice of doing stuff together online. Just today I received an email from one of the people who took our workshop and he wrote “I still remember your course as one of the absolute best courses in my life. Thanks.”I believe our success was because we were passionate about this new form of human interaction.
The second seminal experience was taking part in George Por’s “Knowledge Ecology University” or KEU as we called it, and the relationship forming event of the KE Fair. This was where I had the amazing opportunity to co-facilitate an online workshop with Mihaela Moussou (now Michele Paradise). Michele and I built on the foundational work of Lisa Kimball (then of Metanet, now of GroupJazz) and began to articulate the practice of doing stuff together online. Just today I received an email from one of the people who took our workshop and he wrote “I still remember your course as one of the absolute best courses in my life. Thanks.”I believe our success was because we were passionate about this new form of human interaction.
- From Michele, I learned the concept of “warm electronic communication” and developed deeper insights into the effect of these practices on the experience. Computer mediated – yes, but human driven. Over the years, this initial online learning experience formed the roots of my practice as a designer and facilitator of online learning events.
- Now technology enables far more than the discussion forums of the late 90’s. Thanks to social media we have everything from formal courses to networks on Twitter to facilitate “here and now” learning at any moment we desire (and some we may not desire!) But regardless of the technology, how we use it always matters.
- Conversation and content is at the core of the interactions, build on the foundation of relationship. Now though, relationship can start as a content mediated intersection and then become personal. It used to be the other way around almost exclusively. An interesting change. New social media that helps tag, sort and reuse content has been key to this change.
Communities of Practice and Learning
 Through KEU I met Etienne Wenger and John Smith, who opened my eyes to the fact that I have been embracing community learning and communities of practice most of my life. I was simply unaware of the label, the research and scholarship around these things we call “CoPs.” Back in the late 90’s technology was just used for distributed Cops – folks who could not physically be together. Now technology is nearly pervasive for most communities in the developed world, colocated or not. We take it for granted that we’ll schedule, learn, work and play together assisted by social media. It has matured from an oddity and an outlier to a given.
Through KEU I met Etienne Wenger and John Smith, who opened my eyes to the fact that I have been embracing community learning and communities of practice most of my life. I was simply unaware of the label, the research and scholarship around these things we call “CoPs.” Back in the late 90’s technology was just used for distributed Cops – folks who could not physically be together. Now technology is nearly pervasive for most communities in the developed world, colocated or not. We take it for granted that we’ll schedule, learn, work and play together assisted by social media. It has matured from an oddity and an outlier to a given.
My key learnings about social media and communities:
- More significant that utility, social media has changed what it means to “be together.” It has changed our experience and understanding of being part of a group, a community or a network. It has created a massive multiplier of the options we now have to be with other people. This is heaven and hell. Heaven because we can access knowledge and relationship like never before. Hell because in our multi-membership, we dilute relationship, become overwhelmed, or fall into group mind narrowness by only associating with those who think like us – just because we can. Social media enables this.
- As with online communities, learning communities benefit from facilitation, both formal and informal, designated or spontaneous and self-generated. “Build it and they will come” continues to be a fallacy with each new wave of social media. However, the facilitative practices must evolve in conjunction with the software. Things change on all sides.
- The deeply embedded nature of technologies in communities has given rise to the role and function of technology stewardship, the work of people who know enough about their community and enough about technology to help pick , configure and use technology to support community activities. This has become a central practice and learning focus in my life. See book writing below…
Global Networks & Knowledge Sharing
 In 2000 I put it out to the universe that I wanted to work internationally. The internet was connecting me to people far beyond my personal geography and so enhancing my life, I wanted more. I was on an email list about online communities when someone in Turkey asked if anyone wanted to come to Turkey and talk about online communities. I said yes. The universe answered. Then it was Azerbaijan, Georgia (the country), Armenia, Kenya, South Africa, Indonesia, Columbia, Ghana, Ethiopia, and a multitude of international NGOs based in Europe and North America who gave me the opportunity to apply online interaction and collaboration practices in the field of international development.
In 2000 I put it out to the universe that I wanted to work internationally. The internet was connecting me to people far beyond my personal geography and so enhancing my life, I wanted more. I was on an email list about online communities when someone in Turkey asked if anyone wanted to come to Turkey and talk about online communities. I said yes. The universe answered. Then it was Azerbaijan, Georgia (the country), Armenia, Kenya, South Africa, Indonesia, Columbia, Ghana, Ethiopia, and a multitude of international NGOs based in Europe and North America who gave me the opportunity to apply online interaction and collaboration practices in the field of international development.
The most amazing aspect of this work, going back to 2001 until today, was the different attitude of people outside of North America and Europe – people who heretofore did not have the ability to connect and learn outside of their village, town or city. While Americans would complain about the technology, the time, and anything, my African colleagues would overcome horrid bandwidth and intermittent electricity to participate. They invented ways to leap across the barriers, innovating with mobile technology, translating community and tribal practices into online environments and getting things done.
- When the door to connection is open, watch who walks through and follow them, not those who stand at the doorway and naysay! And I’m not just talking about social media early adopters. I’m talking about people passionate about getting something done.
- Social media offers us incredible intellectual capital opportunities to link up the best and often most diverse minds to address a problem or opportunity. The challenge is that this opportunity may lead us to feel overwhelmed and we are often unprepared to usefully use the diversity of the world and can easily retreat to our familiar territory and group think. The strategic use of social media to stretch us to our edges and immerse us in that diversity is centrally important.
Weaving across Silos
 As I dove deeper into knowledge management and knowledge sharing in international development, social software was growing, changing and evolving. Through this work I also connected with a specific community, Knowledge Management for Development or “KM4Dev” which turned out to be one of my most important CoPs. Through KM4Dev I continued (and continue) to learn but more importantly become part of a network of people working in international development. Our relationships – across organizations, countries, even language – became a new resource to share knowledge, learn together, and reduce duplication where it made sense (as in making a shared knowledge sharing toolkit) . I can’t prove this, but I think our network has actually contributed to more cross organizational cooperation and better use of resources.
As I dove deeper into knowledge management and knowledge sharing in international development, social software was growing, changing and evolving. Through this work I also connected with a specific community, Knowledge Management for Development or “KM4Dev” which turned out to be one of my most important CoPs. Through KM4Dev I continued (and continue) to learn but more importantly become part of a network of people working in international development. Our relationships – across organizations, countries, even language – became a new resource to share knowledge, learn together, and reduce duplication where it made sense (as in making a shared knowledge sharing toolkit) . I can’t prove this, but I think our network has actually contributed to more cross organizational cooperation and better use of resources.
- Social media keep networks, their content and activities knitted together. Networks weave across people and organizations. So social software + networks = change and even transformation. (One of these days it would be worth writing about the difference between change and transformation!)
(Drawing) Pictures
 After years of words, words, words, something was beginning to dawn on me. I missed pictures. I missed art. I realized that all those little drawings and head shots I inserted into forum posts meant more to me and others than I had realized. Then I took a massive tumble offline to learn about visual thinking and visual practices, specifically graphic recording and graphic facilitation. These new practices not only transformed my offline work, but have impacted how I use social media. Specifically,
After years of words, words, words, something was beginning to dawn on me. I missed pictures. I missed art. I realized that all those little drawings and head shots I inserted into forum posts meant more to me and others than I had realized. Then I took a massive tumble offline to learn about visual thinking and visual practices, specifically graphic recording and graphic facilitation. These new practices not only transformed my offline work, but have impacted how I use social media. Specifically,
- I’m consciously including visual methods and practices, particularly in synchronous online work, made possible by new visual tools such as shared mind mapping, and better online whiteboards.
- Tapping the incredible content of networks like Flickr and the practice of Creative Commons licenses to use that content.
- Appreciating and including visual and aesthetic elements in any social software deployment work I do. A case in point was the impact of the “baby friendly” redesign of the hugely successful ShareYourStory online community for parents with babies in the neonatal intensive care unit.
Blogging and Doing Business
 Little did I think when I began this blog in 2004 that my blog would a) reveal the network I didn’t know I had and b) give my work visibility that helped me grown and deepen my consulting work. I had tried a few experimental project blogs with clients in early 2001 and 2002 and they did not root into the work. So I began again in 2004, mostly because I can’t talk and write about a social media tool until I have used it in practice. I was a total skeptic but in the first month, something happened. People who I didn’t know knew my work. They “knew” me. The work I’d been publishing on my little hand made website was alive in the world. Now the blog gave a channel for people to respond, to critique and reciprocate. I was blow away. The blog made the network visible.
Little did I think when I began this blog in 2004 that my blog would a) reveal the network I didn’t know I had and b) give my work visibility that helped me grown and deepen my consulting work. I had tried a few experimental project blogs with clients in early 2001 and 2002 and they did not root into the work. So I began again in 2004, mostly because I can’t talk and write about a social media tool until I have used it in practice. I was a total skeptic but in the first month, something happened. People who I didn’t know knew my work. They “knew” me. The work I’d been publishing on my little hand made website was alive in the world. Now the blog gave a channel for people to respond, to critique and reciprocate. I was blow away. The blog made the network visible.
The second great value blogging gave me was a place to “think out loud” with my network, to offer half-baked ideas and solicit help to finish baking them. It is the easy-bake oven of learning. Write, hit post, and you are in the learning lab.
From this transparency, this “showing my work” in public I have gained new collaborators and clients. I have a visible track record of my thinking and work that people can peruse and evaluate. I find I now attract clients with whom I am a good fit and avoid those that would not create a productive partnership. My online identity serves me well. Flickr, Twitter and other social media tools now augment and enhance the blog – often woven into the blog with widgets. 80% of my working time is mediated using social media, from Skype, Google Docs, Twitter, Drupal, Moodle, Elluminate and an every changing myriad of other tools.
- Social media is an amazing (and sometimes scary) set of tools to show your identity online. We have to learn more about what this means and its implications going forward.
- Tools that help us visualize our networks is a key to tapping those networks.
- I can’t imagine doing 90% of the work I do now without social media. Like it has for me, social media has enabled a wave of small and entrepreneurial business. I’m grateful.
- Early supporters gave my blog exposure and me encouragement. Reciprocating the generosity of others is easy with social media – DO IT!

Writing a Book
As I noted, communities of practice gave a language, a name for so much of what I do. In 2004 Etienne came to John Smith and I and asked if we’d help him update a little report he wrote in 2001 on technologies for CoPs. We said sure. What started as a report revision grew slowly (and sometimes painfully) into what is now Digital Habitats: stewarding technology for communities which will come out this month. The book was written by the three of us primarily at a distance. Without Skype, email, Google docs, Flickr, and publishing on demand, this book would not have been born. We had only three face to face sessions.
- Social media provides an amazing research, testing and writing environment.
Liberating my inner geek
As the visual practice has liberated my inner artist, social software has liberated my inner geek. Particularly as a woman of 51 years of age, this enormous software playground has given me a way to bend stereotypes of middle aged white women and technology. I look proudly at my mom who at 79 is rediscovering high school friends on Facebook and enhancing volunteerism through web tools. Today’s tools are friendly enough to put hands on and just try. To experiment without high risk of either failure or humiliation. They can get a lot easier, but they have unleashed many inner geeks. This is true across generations and the impacts are significant on our culture and our world. I think if this blog post from Lisa, who I met in June at an educational tech conference in Hawaii. She wrote:
ED-MEDIA 2009 « Lisa’s (Online) Teaching Blog
My first technology-related experience, however, was on the plane getting here from San Diego. The flight was 5 1/2 hours, and during that time total strangers sat next to each other without ever introducing themselves, sharing adjacent space. Gradually I noticed some children giggling nearby. I looked over and they were, I thought, playing Nintendo. But when I peeked, I saw that they were writing on the screen, and I soon realized that many children on the plane had Nintendos and were using its wi-fi pictochat feature to write to each other. After an hour or so, children were exchanging information about their seat locations, and were getting up and saying hi. At one point there were kids standing in the aisle and the flight attendant had to ask them to sit down so she could serve food. By the time they had to shut off their devices for landing, they knew where everyone was staying in Hawaii and had arranged playdates if their hotels were near each other, forcing the parents to actually meet each other. The kids used technology to create society on the plane, where adults only endured the enforced company of others.
 So what are the patterns?
So what are the patterns?
First, it has been useful for me to recognize that social media has a role in my life as an individual, as a member of communities and groups, and as a participant in these wider, free-ranging things we call networks. Individual – Group – Network -> the whole spectrum. I find this amazing.
Second, my activities can be loosely grouped into the following.
- Learning
- Getting work done
- Finding and connecting with people
- Getting stuff (search, content, etc.)
- Exploring and pushing my own boundaries
My practices have been radically changed and shaped – yes, even transformed – by social software.
I never would have imagined this back in November, 1996. Thanks, Howard! (edited to correct date from 2006 to 1996)
(P.S. In a future post I might try and document the configuration of tools that I use in these practices. But now it is time for lunch!)

 This afternoon I’m spending a half hour on a Skype video conversation to share a bit of how I use social media. I figured it would be good to exercise my memory a bit and unearth some of the key stories that led me to to my social media use today, and perhaps surface some of my patterns. The history approach also shows that while the term “social media” was not in play when I jumped in, the social use of online media has been growing for many years – well before my online time. These roots are significant because our patterns of use, our ways of embracing or rejecting technology are grounded in this history.
This afternoon I’m spending a half hour on a Skype video conversation to share a bit of how I use social media. I figured it would be good to exercise my memory a bit and unearth some of the key stories that led me to to my social media use today, and perhaps surface some of my patterns. The history approach also shows that while the term “social media” was not in play when I jumped in, the social use of online media has been growing for many years – well before my online time. These roots are significant because our patterns of use, our ways of embracing or rejecting technology are grounded in this history. My first real step into what we now call social media was logging on to Howard Rheingold’s “
My first real step into what we now call social media was logging on to Howard Rheingold’s “ “Eminds” was where I learned that online relationships can be real, how they get real, and how they break and fail. It was in “helping” “save” the community after Howard lost funding that I had my first big online facilitation failure. This taught me about both the similarities and differences of group dynamics online and offline. It was my urgency to figure this out that set me on my professional path as a practitioner and learner about online facilitation. I knew from that experience that whenever we talked about technology (social media) we needed to also talk about practice and the human beings doing the practicing. It was life changing.
“Eminds” was where I learned that online relationships can be real, how they get real, and how they break and fail. It was in “helping” “save” the community after Howard lost funding that I had my first big online facilitation failure. This taught me about both the similarities and differences of group dynamics online and offline. It was my urgency to figure this out that set me on my professional path as a practitioner and learner about online facilitation. I knew from that experience that whenever we talked about technology (social media) we needed to also talk about practice and the human beings doing the practicing. It was life changing. The second seminal experience was taking part in George Por’s “Knowledge Ecology University” or KEU as we called it, and the relationship forming event of the
The second seminal experience was taking part in George Por’s “Knowledge Ecology University” or KEU as we called it, and the relationship forming event of the  Through KEU I met
Through KEU I met  In 2000 I put it out to the universe that I wanted to work internationally. The internet was connecting me to people far beyond my personal geography and so enhancing my life, I wanted more. I was on an email list about online communities when someone in Turkey asked if anyone wanted to come to Turkey and talk about online communities. I said yes. The universe answered. Then it was Azerbaijan, Georgia (the country), Armenia, Kenya, South Africa, Indonesia, Columbia, Ghana, Ethiopia, and a multitude of international NGOs based in Europe and North America who gave me the opportunity to apply online interaction and collaboration practices in the field of international development.
In 2000 I put it out to the universe that I wanted to work internationally. The internet was connecting me to people far beyond my personal geography and so enhancing my life, I wanted more. I was on an email list about online communities when someone in Turkey asked if anyone wanted to come to Turkey and talk about online communities. I said yes. The universe answered. Then it was Azerbaijan, Georgia (the country), Armenia, Kenya, South Africa, Indonesia, Columbia, Ghana, Ethiopia, and a multitude of international NGOs based in Europe and North America who gave me the opportunity to apply online interaction and collaboration practices in the field of international development. As I dove deeper into knowledge management and knowledge sharing in international development, social software was growing, changing and evolving. Through this work I also connected with a specific community, Knowledge Management for Development or “
As I dove deeper into knowledge management and knowledge sharing in international development, social software was growing, changing and evolving. Through this work I also connected with a specific community, Knowledge Management for Development or “ After years of words, words, words, something was beginning to dawn on me. I missed pictures. I missed art. I realized that all those little drawings and head shots I inserted into forum posts meant more to me and others than I had realized. Then I took a massive tumble offline to learn about
After years of words, words, words, something was beginning to dawn on me. I missed pictures. I missed art. I realized that all those little drawings and head shots I inserted into forum posts meant more to me and others than I had realized. Then I took a massive tumble offline to learn about  Little did I think when I began this blog in 2004 that my blog would a) reveal the network I didn’t know I had and b) give my work visibility that helped me grown and deepen my consulting work. I had tried a few experimental project blogs with clients in early 2001 and 2002 and they did not root into the work. So I began again in 2004, mostly because I can’t talk and write about a social media tool until I have used it in practice. I was a total skeptic but in the first month, something happened. People who I didn’t know knew my work. They “knew” me. The work I’d been publishing on my little hand made website was alive in the world. Now the blog gave a channel for people to respond, to critique and reciprocate. I was blow away. The blog made the network visible.
Little did I think when I began this blog in 2004 that my blog would a) reveal the network I didn’t know I had and b) give my work visibility that helped me grown and deepen my consulting work. I had tried a few experimental project blogs with clients in early 2001 and 2002 and they did not root into the work. So I began again in 2004, mostly because I can’t talk and write about a social media tool until I have used it in practice. I was a total skeptic but in the first month, something happened. People who I didn’t know knew my work. They “knew” me. The work I’d been publishing on my little hand made website was alive in the world. Now the blog gave a channel for people to respond, to critique and reciprocate. I was blow away. The blog made the network visible.
 So what are the patterns?
So what are the patterns? It seems like we just finished the last one, but here it comes again… the next
It seems like we just finished the last one, but here it comes again… the next 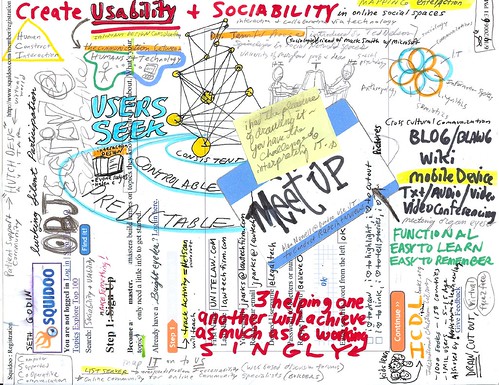
 Community Leadership and Facilitation
Community Leadership and Facilitation Social networks, particularly
Social networks, particularly  Reflective Practice
Reflective Practice