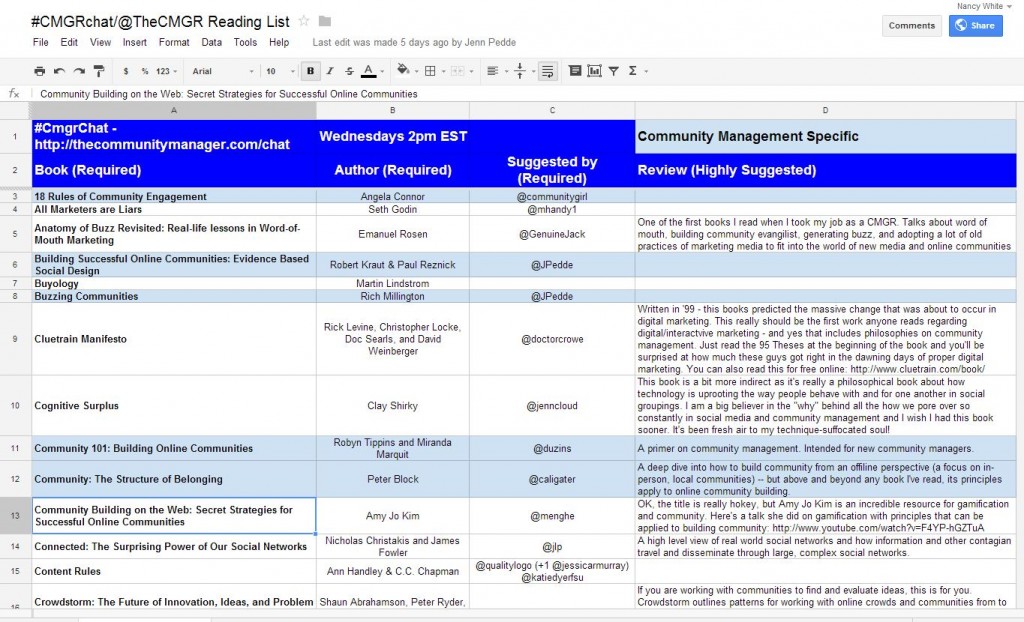
Lurking, or the practice of entering into online spaces to read, but not to post or “visibly participate” has been a perennial topic wherever and whenever online interaction comes up. I was combing through some old resources in preparation for a series of brown bag gatherings I’m leading in the next few months, and came across this gem of a summary from the Online Facilitation group (now mostly dormant) that I’ve hosted since 1999! I am recopying the notes here as a more visible, accessible archive. This is Chris Lang’s compilation of a discussion that took place on the Online Facilitation Listserv July 25-August 8, 2003. He wrote: “Please excuse my editorial license—the postings can be found in their completeness in the archives at http://groups.yahoo.com/group/onlinefacilitation/messages” Alas, some of the links are now dead. I’ve tried to find substitutes where possible. See also References on Lurking from 2010 on this blog!
Lurking, or the practice of entering into online spaces to read, but not to post or “visibly participate” has been a perennial topic wherever and whenever online interaction comes up. I was combing through some old resources in preparation for a series of brown bag gatherings I’m leading in the next few months, and came across this gem of a summary from the Online Facilitation group (now mostly dormant) that I’ve hosted since 1999! I am recopying the notes here as a more visible, accessible archive. This is Chris Lang’s compilation of a discussion that took place on the Online Facilitation Listserv July 25-August 8, 2003. He wrote: “Please excuse my editorial license—the postings can be found in their completeness in the archives at http://groups.yahoo.com/group/onlinefacilitation/messages” Alas, some of the links are now dead. I’ve tried to find substitutes where possible. See also References on Lurking from 2010 on this blog!
The subject of the discussion was originally how to deal with “lurkers”, but a variety of other terms for it were suggested: “wall flower”, “non poster”, “legitimate peripheral participation”. For easy indexing, I have divided stuff into 54 pieces in 7 categories:
- 4 Other Resources
- 5 Considerations on Naming the Phenomenon
- 6 Arguments That Facilitators Should Try to Increase Posting
- 20 Ways to Increase Posting
- 10 Arguments That Facilitators Should Not Try to Increase Posting
- 4 Ways to Figure Out How Many are Reading But Not Posting
- 5 System Changes to Physically Allow Greater Participation
4 Other Resources
- Understanding lurkers http://www.centrinity.se/Conferences/Nerladdning/000231AE-80000001/00A03C2A-001E85B5.9/ This is a one page document, identifies three main types of lurkers and gives specific strategies (alas, link is dead – nw)
- Involving Lurkers in Online Discussions http://www.teachingonthenet.org/articles/involvingLurkers.htm Comments from lurkers, in the context of courses that include an online discussion component. Here, the questions are mostly about whether to penalize lurkers and whether to make contributions to the discussions a strict requirement.
- Shedding light on Lurkers in Online Discussions http://www.ifsm.umbc.edu/~preece/paper/16%20Shedding%20Light.final.pdf A little old (1999), based on a study. Again, understanding why people are not posting is key to selecting the appropriate strategies to make them post more. (This link is working for me… a cached file) (more from Preece and Nonnecke on lurking here, here and here. There is a nice article from Kate Crawford: Listening, not Lurking. NW)
- Let’s get more positive about the term ‘lurker‘, http://groups.yahoo.com/group/onlinefacilitation/files/LurkerProjectCoPWorkshopSPring03a.doc (A copy can also be found here for those who are not members of the Onfac list http://www.groups-that-work.com/GTWedit/GTW/lurkerprojectcopworkshopspring03rev.pdf) MacDonald, J.., Atkin W., Daugherity F., Fox, H., MacGillivray, A., Reeves-Lipscomb, D., Uthailertaroon, P. (2003) CPsquare Foundations of Communities of Practice Workshop : The Value of Lurking, Resistance to Lurking, Why Lurkers Lurk, The Importance of CoP Context, Methods for Helping CoPs and CoP Members Flourish, Measuring and Defining LPP: Questions and Ideas
5 Considerations on Naming the Phenomenon
- “Lurker” is a negative word isn’t it? We’ve given it negative connotations for some reason. But some people don’t like being called “wallflowers” either. But if in this context we just accept the word “lurker” as meaning someone who is part of a virtual group but doesn’t participate, are you ok with it?
- But to use the term ‘lurking’ with its disparaging connotations in the same breath as ‘appropriate environment’ is at least rather oxymoronic. I know it’s been done to death, but it’s a matter of ‘call me a lurker, and I’ll hide even deeper.
- I personally find the term “lurker” extremely offensive, objectifying and insulting. I can not believe that an “educated” list such as this can not be more sensitive to the “labels” they use. I believe it would be kinder to use the term “non poster” or come up with a kinder gentler term that gives the non poster credit for his passive participation. –Kathleen Johnson
- There are negative connotations for just about every noun, verb and adjective. I don’t believe that lurker carries the pejorative weight of degree, of say, a racial epithet and even there are degrees of escalating severity and consequences. I can certainly see evidence to the contrary that use of a racial epithet is not likely to lead to less participation, IRL there are those who would become confrontational and ask for redress.
- “Learning viewed as situated activity has as its central defining characteristic a process that we call legitimate peripheral participation. By this we mean to draw attention to the point that learners inevitably participate in communities of practitioners and that the mastery of knowledge and skill requires newcomers to move toward full participation in the sociocultural practices of a community. ‘Legitimate peripheral participation’ provides a way to speak about the relations between newcomers and old-timers, and about activities, identities, artifacts, and communities of knowledge and practice. It concerns the process by which newcomers become part of a community of practice. A person’s intentions to learn are engaged and the meaning of learning is configured through the process of becoming a full participant in a sociocultural practice. This social process includes, indeed it subsumes, the learning of knowledgeable skills.” from p. 29, J. Lave, E. Wenger. Situated Learning : Legitimate Peripheral Participation, New York, Cambridge University Press, 1990. The way ‘Legitimate peripheral participation’ has begun to be used…(Nancy’s take on it!) … that being on the periphery is OK and that there is an always changing pattern of how we choose to participate and learn in a group. If the topic is near and dear to me, I move towards a more active role, closer to the center. If it is of less interest or I feel I don’t have something substantive to contribute, I remain more of an observer on the periphery. My self-placement from the periphery to the core may have to do with newcomer/old-timer status, or it may have to do with interest, expertise, available attention.
6 Arguments That Facilitators Should Try to Increase Posting
- …in my opinion, if you join a community, you have an obligation to “give back” for all the jewels you’ve taken away. Once again I qualify that statement with the caveat that no one is expected to reply to every topic. But when you feel you have something to offer–go for it.
- Full participation (two-way interaction) is critical when:
- – making a (shared) decision that will affect the group
- – gathering feedback from an intentionally-diverse stakeholder group
- – attempting an innovation through collaboration
- – the member is officially representing a minority interest group (by number or specific point-of-view, or interest area)
- – the member represents an assumed responsibility (2 definitions: either updating the status of a task, or representing a point-of-view about which many others make assumptions.)
- “A community thrives on “giving back” behavior and widespread participation in community building efforts.”
- “The law of reciprocity applies to lurking, learning, and linking to more lurking and learning. One can be a recipient for only so long. Fairness dictates that one needs to give back something of comparable value. The giving back does not have to occur in the original forum.”
- We are all peripheral participants at some time or another, so I think we should also be active participants at some point or another. It’s ok to be a Peripheral Participant, but it’s also good to give back to the community.
- My question is how to understand in any group the role of legitimate peripheral participation and how to make the POSSIBILITY of moving from the periphery to the core available without unnaturally FORCING it because legitimate peripheral participation may be the right thing at the time for any individual. In a list like this, I feel invitation alone (a thought provoking post, a request to self introduce) is sufficient and that if someone wants to stay on the periphery, that is totally cool. IN a virtual team where each members contribution is critical to goal achievement, legitimate peripheral participation becomes something I’d pay more attention to and actively work to bring the full team closer to the “center.” –Nancy
20 Ways to Increase Posting
- In a face-to-face meeting, the facilitator will ask the group from time-to-time if there are any comments from people who haven’t spoken yet. The same technique works just fine online, too, with some graceful welcoming language. — Arnie Anderson
- Use introductions. It is important, however, that the community then express an interest in them right away.
- Imagine if subject headers not only listed the abbreviation for the email group, the kind of post, and the name for the thread, but also the number of the post on that thread. For example, “Subject: [of] 1 TIP – Non-Posters” could indicate that this is the first post in the “Non-Posters” thread of the onlinefacilitation group, and this is a TIP thread. If I knew it was the first post, then I wouldn’t be afraid that I missed previous posts.
- Have group members partner-up and get to know each other. It can be easier to participate in a group when you know you’ve got a friend there. It can be important to have a peer, rather than a professor, to go to.
- In the community I run, I find that a telephone call can be enough to turn a non-poster into a talker. Sometimes the “voice to voice” connection makes the community seem more real to a non-poster, enhancing her investment in the group.
- Set up a discussion about “Why aren’t people participating in this group?” This establishes that you care, and makes it explicit that it is not wrong for non-posters to post. But be careful–if you make this threatening, it could drive people away!
- Sometimes stop and ask the whole group what they have learned or gained. This gives people a second chance to jump in.
- On several of the Listservs of which I am a member, I used to conduct lurker amnesty day. Calling attention to the lurker behavior and providing an avenue for them to de-lurk is often enough to bring them out. The ploy is not without controversy with some folks who object to the connotations associated with “lurker”. It will often bring up a discussion on group values around participation in the discussion. Still, lurker amnesty day has always been effective–meaning people do come forth and post for the first time. (But Artur warns: Talking about “lurkers” is not usually “good facilitation” because after that some lurkers will participate more – but many others, lurkers and not, will quit.)
- Make sure there are shared expectations about what/how people interact in the group, and who is supposed to be posting. Sometimes as organizers and facilitators it seems obvious, but when I’ve checked my assumption about people’s understanding, I’ve often been very surprised at how “unobvious” it is.
- One thing that can keep me from posting is that I haven’t read all of the previous postings, and I’m afraid to post something that has already been addressed. Threads help, but this wiki is even better because it sorts the threads–just like brainstorming around a flip chart 🙂
- Read without TOO much judgment
- There are quite a few groups where I am lurking 99% of the time and suddenly someone will post something that will trigger me to post a response. If you can find that something for these women, they might start with one post and be encouraged to continue (especially if they get a warm welcome and supportive feedback from the group and the moderator). — Barbara Fillip
- Express interest in them. Ask someone by name if there’s something they want to talk about. – Ann
- In the work I do online, we explicitly use anonymous discussions for some issues. This is not so much a trust issue as 1) a way to flatten the playing field and 2) an encouragement to participate. If the emphasis of the exercise is on gathering group data, rather than who said what, AND if there is an expectation that the group wants as wide-as-possible input from different kinds of stakeholders, then we find there is a great deal of participation.
- I sent a two-question survey to all the participants. The first question (check all that apply) asked them why they were not participating, and the second asked the participants to suggest something I could do to make the experience more useful to them. – Barbara
- I contacted a couple of participants based on what I already knew of their area of expertise and ongoing involvement in projects that we needed to discuss this week. –Barbara
- One of the suggestions is to find a way to reduce the number of postings. This may sound counterintuitive but sometimes if there are too many messages or messages are too long, a good number of participants will find it difficult to keep up with the flow of the conversation and then it’s difficult for them to jump in. As Rolf put it “I pick up new ideas and insights, but the volume of messages is just too high to really feel like ‘replying’ here.”
- Nancy’s light touch facilitation allows a wide variety of ways of participation (as do we the members).
- I think that projects aiming at increasing participation are more likely to succeed if they target people who are already active participants in other communication forums, online or off, rather than attempting to increase the posting volume of those who have shown a preference for little or no posts.
- Don’t let people hide in corners. As Noreen put it: “once you get a spot in the corner it is four times as hard to walk up to someone and make conversation.”
10 Arguments That Facilitators Should Not to Try to Increase Posting
1. Artur wrote: IMHO there are no lurkers!
No one is “hiding” to prepare to “assault” our knowledge or to profit from those who share. In public lists the “public” that subscribe may have many reasons for staying in the list and not contributing. Some are readers but many just don’t have the time for even reading, except very infrequently. And they have the legitimate right to be in that situation as long as they want – except when that is clearly stated in the “definition” of the forum. And they also have the right to begin participating when they feel the need for that or to quit the list at any moment.
Many of us have participated in “Professional Congresses” before the Internet time – and after. What was (is) the percentage of participants
that would present a paper? 1%? 2%? And what was the percentage of people that would put a question or discuss something during discussion time? 3%? 5%? 10%? (and what percentage would offer to serve at the Directions of Professional Associations?)
And would we call the other 90% “lurkers”? Of course not. First because they “showed up” for the meeting. Second because they were the professional body that made possible for the presenters to present something. Third because in some cases they had paid for the Congress – they were the “costumers”! And, of course, if they were present in the sessions, they would hear, they would learn, they would discuss with each other during the coffee breaks (normally the most interesting parts of any Congress) or in private conversations. And after the Congress, they would apply their knowledge and eventually some of them would later present their own papers.
Of course, no one would worry to “facilitate” the participation of the “non-speaking participants” or criticize them as indeed they were the “customers” of the event. And after all, the “logic” of Congresses would be impossible if all the people would participate – there would not be enough time for presentations – or the Congress would need one year – which was obviously too much as someone would need to work after all…
And no one would even question why were the “participants” not presenting papers or putting questions. That was their “right”. What could be questioned was the motivation of the presenters (especially when they would make bad presentations) or the motivation of the people that asked questions (especially when they were silly or trivial ones). Yes, THIS needs an explanation: why do presenters present? For the sake of sharing knowledge? For the sake of prestige? For having their two minutes of exposure? But I never heard a presenter in a Congress saying – I hate those “lurkers” that come here to profit from the knowledge I am creating – if they were creating any knowledge at all, which was not always the case.
2. The member who contributes sometimes but has good insight may be more valuable than someone who has a lot of chatter.
3. Frank “mused”: Seems that if there’s no one giving, there’s no one receiving. So don’t we each have a responsibility (I know, a big word) to be givers of whatever we can if we also long to receive? Else, the well runs dry feeding many from a few. Does that make many of us “parasites” or “users”? Or worst yet, “abusers”?
Seems to me that community is all about “we”, not just “me”. And if I “show up” however I can whenever I can in a way that can be received by others, then I’m a real part of the community. Hmm, and maybe just being a reader brings enough energy to exchange with those who have words (authors) that long to be read.
Why did the authors “show up” in the way that they did? What real need is being filled here for them? Is it truly possible that someone who volunteers to be “in community” has nothing to give? Doubt it. Can we have a yin without a yang? Is there a palpable experience of “silent giving back” in an online community? What would the other end (the reciprocal) of that silent giving back look like? And how do we consciously move from being a “group” to being a “community”?
4. “Are they talking about me? Am I a lurker?” I guess the answer to both questions is yes. And I am not ashamed or apologetic about it. I will speak when I have what I think is a valid question or when I have something valuable to contribute to the conversation. Up until this point I have had neither. While I find the topics of general interest so far, they have not really answered any critical needs or triggered any startling insights that I needed to share. As facilitators, we all know that participation is a wonderful thing and we want to be inclusive, but trying to trigger participation just for participations sake is not desirable in every situation. And my gut tells me that in an online environment, just responding to emails, with nothing to offer, only for the sake of being participative, or being part of the community, just doesn’t feel appropriate. If every person contributed to every email query, just to participate, I would find it aggravating. — Charles A. Tweedly
5. My approach with this list reflects a value that I hold about giving. We may not always directly reciprocate one-for-one, but it is important to give. So I may read something on a list and never offer anything, but what I learned there I may share (and give credit to) someplace else. So that the reciprocity is more general to the world, and not just the list group. But I don’t have any expectations that if you read here, you must contribute. And I respect other folks who run other groups who have such expectations. I don’t personally hold them as universal. – Nancy White
6. For me, many lists I’m on are for me like “tv channels” with a more or less “Big Brother” style of programs on: you can have a look at various “communities” and see how they develop, how people interact, who’s in and who’s out, and so on. I sometimes “tune in” and listen/read more carefully on one of the channels, but most of the time, I just zap around, to keep an overview of the various discourses and discussions. — Rolf
7. …the non posting member is probably absorbing the “material” and distributing the acquired material “off list”. Not all members are up to speed of the “lecturers” and are in “learning” mode. Do members have to advise you of their standing on the pyramid of learning? Whether they are at the top or the bottom, does it matter to you? Is there a test given to determine their ability to absorb and distribute? And if the non poster is at the top of the pyramid, what difference does it make if they are just observing and cataloging data? Do they need your permission? Why is that?
The non poster, quite frankly is one of the most valuable members of the team. They do not fill the board with needless posts so they can be seen and heard. They do not write trivial data just so they can get “attention” or “make themselves feel important”. But what they do do is sit back and observe, sifting the information quietly, and in their own way, passing on the information off list. –Kathleen
8. Where I feel I have more of a responsibility to post, culturally this is not always comfortable. –Claire
9. People also have different values. Some feel obliged to respond, to give “something” back. Some do not. Some feel obliged to only give back some *significant value*, if and when they have such to give (it may be never). This is also not a bad thing, if it is recognized that others values may not match your own.
10. Sometimes the active participants get frustrated if they are contributing and they are expecting feedback from other participants and they are not getting it. I would separate the attitude of the active participants from that of the facilitator. I do get very frustrated with lurkers but I try not to let them know that I’m frustrated with them. That might get in the way of encouraging them to participate. It might be more effective to stress to them the potential benefits of participating rather than stress the negative side of lurking. I suppose that’s just the same as looking at a glass half-empty or half-full. The attitude might make the difference. –Barbara Fillip, Knowledge for Development, LLC
Yes, but if lurkers get feedback such as this from other list members, when all else has failed (I try never to use negative if win-win will work), perhaps they’ll start thinking about it.
4 Ways to Figure Out How Many are Reading But Not Posting
1. Some software especially courseware does this- eg Blackboard you can see how many times a particular post has been ‘read’- but that doesn’t count how many times you might read it yourself or whether or not any meaning has been made- nevertheless it is a great comfort for beginners in online courses who are scared that no-one is reading their posts, but then they begin to wonder why no-one responds..so on it goes….
2. Why not place a humorous survey question in posts to the list, perhaps once a month, that are different in request each time, something like the radio announcements that are still aired on occasion (note: these aren’t humorous!): “This is a test of the national emergency radio broadcast system. In the event of a national emergency, this station will cease regular broadcasting and provide….blah, blah, blah. This is only a test.” But in this case, request that people provide a one-word answer to a somewhat silly or serious question back to the list.
3. Statistical extrapolation–use personal email to poll a random sample about whether they read the post. Once you have done this for a few posts, just assume that you get the same readership on similar posts. It would be really nice if some group would conduct studies like this and publish them–perhaps a facilitator newsgroup might be willing? 🙂
4. Instead of putting content in the email, put it on a special site and put a counter on the site.
5 System Changes to Physically Allow Greater Participation
- The slashdot (www.slashdot.org) model is interesting. Random members are assigned as “raters” for a limited time. Each Rater may rate posts they read on a scale from -1 to 5, and label them “Interesting”, “Insightful”, “Funny”, “Redundant”, “Abusive”, and so forth. Posts initially start with a value determined by the ratings of the poster’s previous posts. Readers may filter posts by rating… If you only want to read the gems, set your filter to 5. If you want to read everything, warts and all, set your filter to -1.
- http://www.weblab.org/home.html (Archived site) “Small Group Dialogue”: Divide the group into many overlapping small groups.
- http://www.americaspeaks.org/library/21st_century_town_meetings.pdf “21st Century Town Meeting “: Live groups gather in tables of 10-12 with a trained facilitator and sends comments electronically to a “theme team” that recognizes common themes across the tables and posts them on a large electronic view screen. Then someone addresses all of the tables and instructs them to vote (electronically) on the issues put up by the theme team. This achieved a 100% satisfaction rate at a 5000 person meeting to set priorities on the World Trade Center rebuild.
- http://h2o.law.harvard.edu/index.jsp (Archived site)“Rotisserie”: Everyone posts an answer to a question and a computer program automatically assigns each person to respond to another person’s answer (and bugs them by email until they do) then assigns people to respond to responses (and so forth).
- www.openspaceworld.org Open Space Technology (or Methodology, as I prefer) for meetings offers a completely new way to handle meetings with a much bigger percentage of people participating actively. –Artur
 Tim Bonneman blogged yesterday about the International Association of Facilitators “International Facilitation Week.” He pondered…
Tim Bonneman blogged yesterday about the International Association of Facilitators “International Facilitation Week.” He pondered…