 Candace Whitehead, the Facilitator Support Specialist for the Florida Online Reading Professional Development project funded by the Florida DOE and housed at the University of Central Florida http://forpd.ucf.edu contacted me last month inviting me to participate in a web meeting with the cohort of online facilitators working in learning and particularly around literacy issues. The chance to have a conversation with practitioners is always an automatic YES for me. When we talked, Candace suggested the topic of “engagement.” This blog post is a little bit of “thinking out loud” prior to our conversation later this month.
Candace Whitehead, the Facilitator Support Specialist for the Florida Online Reading Professional Development project funded by the Florida DOE and housed at the University of Central Florida http://forpd.ucf.edu contacted me last month inviting me to participate in a web meeting with the cohort of online facilitators working in learning and particularly around literacy issues. The chance to have a conversation with practitioners is always an automatic YES for me. When we talked, Candace suggested the topic of “engagement.” This blog post is a little bit of “thinking out loud” prior to our conversation later this month.
Some rough definitions…
First, it is helpful to clarify what we mean by “engagement” online or offline. For me, it ranges from active participation in a group activity, to the subtle and often invisible internal engagement of listening, thinking, or taking and using what one hears from a group and applying it within or outside of that group. One one end you have very visible ways to observe and measure engagement. At the other end you rarely even know it exists.
I also believe that we engage with people AND with content. So when we talk about “encouraging engagement online” we should be clear what type of engagement we are talking about. They are different!
That said, I think MOST engagement in both online and offline groups tends towards the invisible side. Think of the quiet person at the party or lecture, the kid on the fringe of the group playing. They are having an experience of being with a group, of experiencing the communications (verbal and non verbal) of the group.
This engagement may be perceived as positive and/or negative. We must let go of the romantic notion that all engagement is positive to the individual and the group as well as the expectation that all online engagement is positive. It isn’t. Trust me on this one!
So why should we care about engagement?
Particularly in the context of learning?
Well, my guess is no engagement = no chance of learning with others or from content. Again, this hinges on my belief that we learn through engagement both with people and content or the myriad of combinations. Many of us learn just fine by ourselves. Many of us need the social aspect of engagement with others to learn, work and play. I’ll leave the academics and people smarter than me to put the proof on the table. I’ll state as a practitioner, engagement is important for learning for individuals and groups. Period.
How do we encourage engagement online?
Now that some very crude and un-scientific definitions of engagement are on the table, let’s look at how we, as facilitators, can encourage engagement online. And how we encourage specific types of engagement in the service of learning. For this blog post, I’ll focus on social engagement, rather than solo learner engagement with content. Because this is what I suspect Candace is looking for!
Social engagement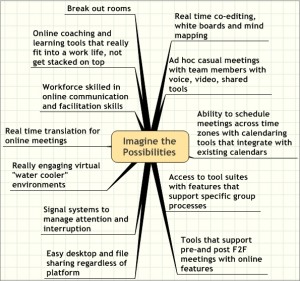
First, remember and use what we know about offline engagement. While these may manifest differently online, we should not forget them. And it is odd, but we often do forget them!
- Address people by name – they are more likely to respond than a generalized comment thrown out to the group. For example, in a web meeting, toss questions both to the group and to individuals.
- Acknowledge and reciprocate contributions given to you as an individual and to the group. This is especially critical for first time contributions. Online, it is a way to indicate that you “heard” someone, which might be a subtle nod offline.
- Ask good questions …. and then shut up and let people answer them! I fail at this one often because I love to ANSWER questions. This is where self awareness and even separation between the role of facilitator and “knowledgable person” (some say “expert.” I resist that a bit.).
- Paraphrase unclear contributions to check for meaning (if you are lost, it is a good chance someone else is!)
- Vary the modality or media to accomodate different needs of participants. Be aware that the way you like to communicate may or may not reflect the needs of others. Vary and see the response to get a sense of what works for individuals and the group. There are always trade offs to accomodate both.
- Nibble. Break up delivery of content and intersperse activities. For synchronous engagements, consider 7-10 minute chunks in your plan. Online, resist the urge to offer pages to read and think in terms of paragraphs. People generally learn in smaller bites. Think of the overeating trap at buffets! Not so nice, even if you grabbed three lobsters, two steaks, a pile of asparagus and 5 chocolate desserts.
- Role model passsion, and your own engagement.
Now, how does this change online? There are two areas that beg for some deeper exploration about engagement, one on the software or tool side and the other on the process side. They are very related, so I’m going to mix them up a bit.
 Offline we have non-verbals and body language to assess the state of people in the room. Online we have to do this with both software and process. From a process standpoint we cannot assume we know the state of the others in the group.
Offline we have non-verbals and body language to assess the state of people in the room. Online we have to do this with both software and process. From a process standpoint we cannot assume we know the state of the others in the group.- For example, silence may mean someone is shy, angry or their microphone doesn’t work –> each of these begs a different facilitation strategy. Process wise, we have to ask more often, to “check in. Build this into your process, especially at the start of an interaction when people don’t know each other and technology issues may not yet be sorted out.
- Use the metrics tools in the software you are using to keep an eye on page views, online indicators, and other measure that can at least tell you if someone has logged on.
- Use “text” and visual “body language” online in your own communications to help others enrich their use of text. Yes, even emoticons, no matter if you don’t like them yourself. They can give tone to text, especially for people who are less experienced at clear writing. (For example: “I am leaned forward towards my screen, devouring this thread, but I’m not sure I undersand fully what you mean by XYZ ” as compared to “What do you mean?” – which could be read in a serious or mocking tone and perhaps leave the other person thinking you don’t care.) I like including images and small audio clips to help assure we are “hearing” each other accurately.
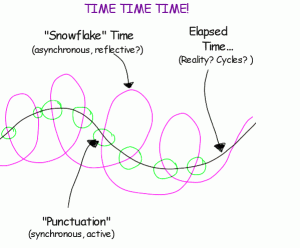
- Time is different online. People who are always on and respond quickly experience online interaction differently than those who log on less frequently. (Gilly Salmon called this ” snowflake time“.) The latter can experience a sense of overwhelm and being “left behind.” Make this dynamic visible to the group and encourage the fast posters to slow down a bit and the others to log on a bit more frequently. Understand that if this gap persists, the group may splinter. If that is the reality, consider sub groups and weave ideas between them as their facilitator.
- Punctuate time. Alternate synchronous with asynchronous as a way to keep the “heartbeat” of a group going. Like a first time runner, groups “heartbeats” have to be faster at first to build relationships, establish norms and patterns of interaction. Over time as the runner “trains” the heart beats slower. So with the group. For example in a three week online workshop I like a minimum of one synchronous telecon interspersed with asynchronous activity. This is a simple matter of attention – which we always find is in short supply!
Yikes, this is getting long. And I haven’t even touched on identity! Maybe it is time to stop and ask how you engage others online? Share with us your useful practices and tips!
 Next in the series of podcasts (previous podcasts linked below) is Sarah Blackmun of the Pangaea Network. Sarah is another long time online colleague and friend from the late 90’s who also seems to connect with others in my network (especially around her studies at the Fielding Institute where we both have a lot of mutual friends.
Next in the series of podcasts (previous podcasts linked below) is Sarah Blackmun of the Pangaea Network. Sarah is another long time online colleague and friend from the late 90’s who also seems to connect with others in my network (especially around her studies at the Fielding Institute where we both have a lot of mutual friends. I’m always interested in where people started in their “practice” no matter what the practice. So I was tickled to be led to
I’m always interested in where people started in their “practice” no matter what the practice. So I was tickled to be led to  Next in the podcast series on social media in international development is a dear friend and colleague, Simone Staiger discussing the design, technology and facilitation of a global e-consultation. Simone is orchestrating 6 regional consultations for the Global Forum on Agricultural Research (
Next in the podcast series on social media in international development is a dear friend and colleague, Simone Staiger discussing the design, technology and facilitation of a global e-consultation. Simone is orchestrating 6 regional consultations for the Global Forum on Agricultural Research ( A DM Tweet today caused me to go and look and see what resources I’ve posted on the blog about
A DM Tweet today caused me to go and look and see what resources I’ve posted on the blog about 


