I’ve been both working with some distributed communities of practice and talking to different folks in my networks about online meeting practices. I’m feeling a resurgence of the kind of interest we saw in the earlier waves of online interaction. There is a pattern that I realize I use, but had not written about it. It is nothing new nor earthshaking, but every once in a while it is worth a moment of reflection and reification.
Many people have been migrating to Zoom for online meetings, both for its ease of use, decent video and chat, but also because it allows breakout groups, something that can be VERY useful for engagement and deeper work. Other groups are adopting tools like Slack and Trello.
So we have new tools. That means we either need new or adapted practices, especially if we are seeking to move away from top down, presentation oriented meetings. (My version of a waste of time!) Here are a few heuristics I’m using to initiate and build the online meeting practices and muscles.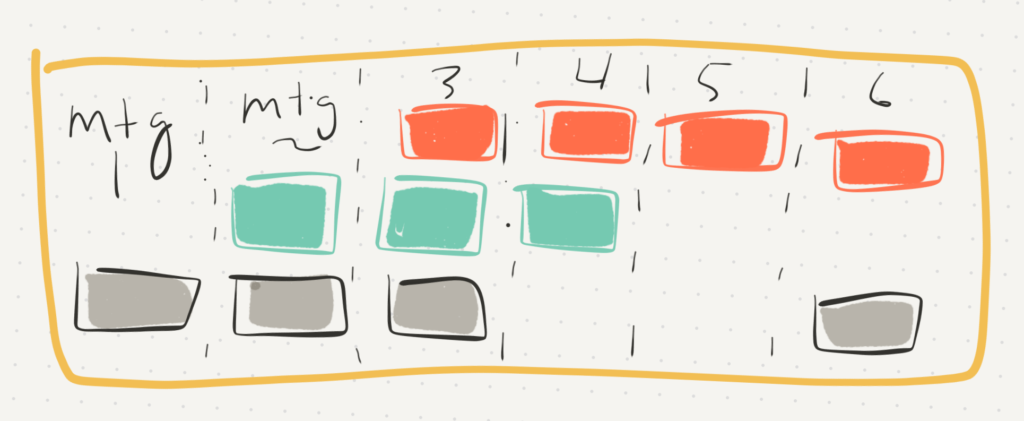
- Experiment/introduce a new practice, then make sure you briefly debrief it. Use it again in the next meeting. It gets easier to do, and the work gets deeper and more meaningful. Encourage people to be curious and withhold judgement until they get to that moment of greater depth. Right now it seems that new practices really bear fruit on the third use.
- In the second meeting of a sequence, use the first practice and add just one more. Then in subsequent meetings you start rolling off some practices to save for when they are most useful, and introduce others. Debrief, practice and then use discernment of what you should stop doing, keep doing, change or start over. This builds an online interaction repertoire.
- Explain just enough so that people interested in using the processes and methods themselves have a starting point to carry the practices elsewhere. Offer links to resources or deep debrief to the interested. Don’t torture the others by droning on about process.
- In debrief, some useful questions can be (drawn from Liberating Structures and elsewhere): what was liberated or enabled by this process? How was it structured? Where else might you use it? These three questions help people be aware the role process plays in their experience, success or failures.
- Finally, don’t expect people, including yourself, to be instantly comfortable and competent with new practices. Take a learning stance. Be an experimenter. Laugh at and learn from failure. If you are leading the charge, role modeling this stance makes a huge difference.
Your ideas? Practices?