 Last Friday I had the great fortune to help facilitate a session at IFAD on SRI, or System of Rice Intensification. My botany degree, while neglected as a career path, has always kept my root interest in plants and ecosystems alive. In the course of doing a graphic recording of the presentation part of the session, a few things kept showing up for me.
Last Friday I had the great fortune to help facilitate a session at IFAD on SRI, or System of Rice Intensification. My botany degree, while neglected as a career path, has always kept my root interest in plants and ecosystems alive. In the course of doing a graphic recording of the presentation part of the session, a few things kept showing up for me.
First, the scholars working on SRI were insistent it was not a proscribed method of growing rice that is useful to poor, small holder farmers, but that it was a set of principles for growing rice and other crops.
A set of principles.
Can we view knowledge sharing not as a proscribed set of practices, but instead a set of principles?
While there are a range of tools and methods that we call “knowledge sharing,” they are just tools. And if we overly focus on them, we miss the point that knowledge sharing is embedded in everything we do. Therefore, to make sure we have time for KS and that we do it well and strategically, we might instead focus on the princples that support KS.
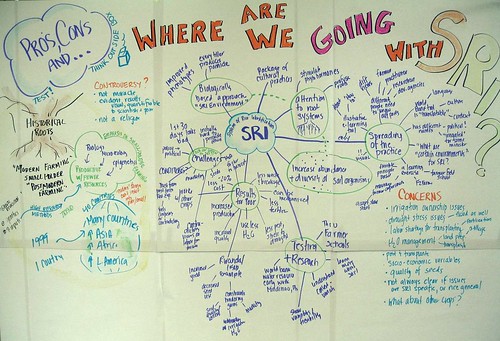
So what might those principles be?
Saturday morning, on my way home from Rome at the unnatural hour of 5:15 am, I was surprised to look up in the airport to see a colleague who was at the joint Share Fair in Rome and a past participant of the online KS workshop I have facilitated for FAO and CGIAR. Justin Chisenga of FAO shared the challenges of KS in agriculture in Ghana. He said there were no precedents for sharing agricultural research, but instead a culture of individual ownership, and thus very often loss, of agricultural research knowledge. Locked up in files or personal computers, and unknowingly discarded upon retirement or death, years of knowledge had leaked away. Ownership, not public good.
- What principles could change from lock down to flow in Ghana?
- What principles could encourage funders to reframe their support towards openness and learning?
- What principles could reframe organizational and national policies to support and reward building public instead of private good in fields that ostensibly are dedicated to things like feeding one’s country, region or world?
- What principles could allow people to share knowledge even in large, complex and necessarily political organizations?
My mind returned to what I learned about SRI. SRI focuses attention on the quality of seed, the timing and method of rice seedling transplantation, and THE HEALTH OF THE SOIL and the microorganisms that live there.
What is the soil for knowledge sharing? How do we know it is healthy? What “transplantation” practices allow us to move fragile new knowledge from one place and allow it to thrive in another, without too much loss, or too much investment in water and fertilizer? How should we “weed” to keep information overload from overwhelming us?
The analogy is intriguing me.
Rice tending image from Wikipedia
 When I was in Singapore for KMSingapore, I was able to visit the offices of Straits Knowledge, where Patrick Lambe, Edgar Tan and Ng Wai Kong do amazing things to help their clients create and share knowledge. I’ve always enjoyed reading their Green Chameleon blog and have greatly appreciated (and envied, I must admit) Patrick’s sketching skills! While in the office, Patrick gave me a hands-on with their Knowledge Toolkit and I said, THIS IS SO COOL, let’s make a quick video to share. So here it is. Please forgive the typos on the text. You know me. Typo queen! I’m going to share this on KM4Dev as well, as i think my colleagues there will really like this as well. So GO SHARE KNOWLEDGE!
When I was in Singapore for KMSingapore, I was able to visit the offices of Straits Knowledge, where Patrick Lambe, Edgar Tan and Ng Wai Kong do amazing things to help their clients create and share knowledge. I’ve always enjoyed reading their Green Chameleon blog and have greatly appreciated (and envied, I must admit) Patrick’s sketching skills! While in the office, Patrick gave me a hands-on with their Knowledge Toolkit and I said, THIS IS SO COOL, let’s make a quick video to share. So here it is. Please forgive the typos on the text. You know me. Typo queen! I’m going to share this on KM4Dev as well, as i think my colleagues there will really like this as well. So GO SHARE KNOWLEDGE! Last Friday I had the great fortune to help facilitate a session at
Last Friday I had the great fortune to help facilitate a session at 
 I have a tendency to destroy my computer headsets/mics with regularity. I run over the cords, the plugs loosen and then the sound degrades. It is time again to buy a new set, but instead of buying the cheapest set at the local office store, I decided to get the recommendations of my network – since many are also frequent users of this product.
I have a tendency to destroy my computer headsets/mics with regularity. I run over the cords, the plugs loosen and then the sound degrades. It is time again to buy a new set, but instead of buying the cheapest set at the local office store, I decided to get the recommendations of my network – since many are also frequent users of this product.